The emergence of 5G as a global language defined by its standards has revolutionized the way we communicate, enabling near-instantaneous connections between sensors, devices, critical infrastructure, and people. Decentralized, high-powered computing and extensive storage resources have become a game-changer for the industry. With the recent surge of interest and early deployments of edge computing, service providers have identified the network edge, close to radio towers, as a natural location for edge computing resources. By bringing computing closer to users and IoT devices, it reduces latency and supports data processing near the data sources. When combined with the powerful capabilities of 5G New Radio, it creates potential solutions for previously unsolvable problems. This powerful combination forms a new toolset for the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
According to recent research, the manufacturing, logistics, and government industries exhibit the highest demand for private 5G technology. These findings align with our observations, as we have seen a surge in demand for Private 5G and Edge Cloud solutions in these sectors.
The study also identified four key themes that are driving the adoption of private 5G technology. These themes include enabling hybrid connectivity, implementing policy and activation for diverse sensor profiles, utilizing advanced intelligence through private 5G and edge computing, and integrating applications and infrastructure to achieve optimal business outcomes. This shift from broad themes to specific applications demonstrates the growing understanding of the benefits that private 5G technology can bring to various industries.
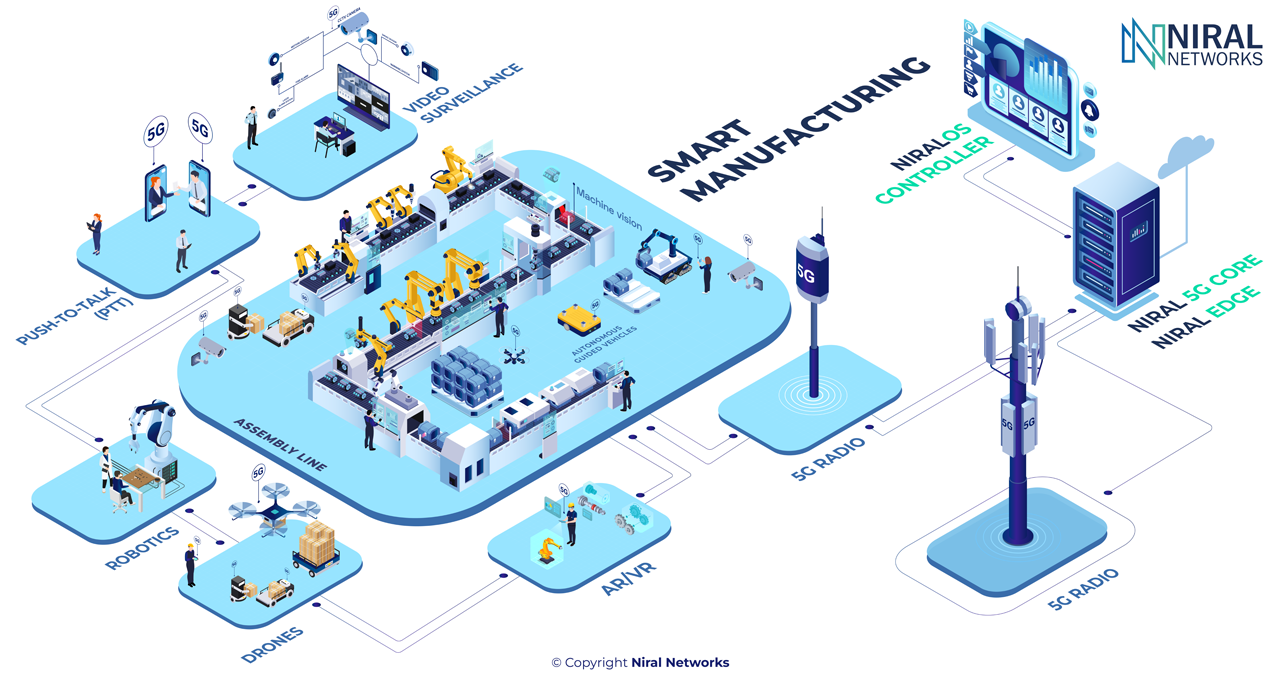
Main areas of applications in the Manufacturing Industry:
- Push-to-Talk (PTT) enables workers to communicate across locations, with real-time location tracking.
- Private 5G supports augmented reality and virtual reality (AR/VR), allowing for self-assist, work-assist, and remote-assist
- Private 5G makes real-time connectivity and control possible for autonomous guided vehicles.
- Computer vision for automatic video surveillance, inspection, and guidance is faster and more efficient on a private 5G network.
- Private 5G Connectivity for Robotics
Connected devices can remain reliably and securely connected to the enterprise network throughout the work shift without relying on Wi-Fi or portable hot spots.
1. Push-to-Talk (PTT), is a critical component of many industries, including manufacturing, construction, transportation, and public safety. With PTT, workers can communicate instantly with their colleagues, regardless of their location, improving collaboration and coordination, and enhancing productivity and safety.
However, traditional PTT systems typically rely on legacy technologies, such as analog radios or 2G/3G cellular networks, which often have limited coverage and reliability, making it challenging to ensure seamless communication across locations. In addition, traditional PTT systems often lack real-time location tracking capabilities, making it difficult for managers to monitor their workers’ movements and respond quickly in case of emergencies.
Private 5G networks offer a significant improvement over traditional PTT systems, providing high-bandwidth, low-latency, and high-reliability connectivity across a wide area. With private 5G, workers can communicate instantly with their colleagues, using voice, video, and data, regardless of their location, improving collaboration and coordination across different teams and departments.
Moreover, private 5G networks enable real-time location tracking, using advanced indoor positionings technologies such as Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), Wi-Fi, and Ultra-Wideband (UWB). With real-time location tracking, managers can monitor their workers’ movements and activities, improving safety, security, and productivity.
For instance, in a manufacturing facility, workers can use PTT to communicate with their colleagues in different departments, such as maintenance, quality control, and logistics. With real-time location tracking, managers can monitor the location of their workers and equipment, ensuring timely responses to emergencies, and optimizing workflows.
In the transportation industry, private 5G-based PTT systems can enable real-time communication between drivers, dispatchers, and logistics personnel, improving coordination and efficiency. With location tracking, managers can monitor the location of their vehicles, ensuring the timely delivery of goods and services.
In summary, private 5G-based Push-to-Talk with real-time location tracking capabilities offers significant benefits to a wide range of industries, improving collaboration, coordination, safety, and productivity. As private 5G networks become more widespread, we can expect to see increased adoption of this technology in various sectors, transforming the way we work and communicate.
2. Private 5G supports augmented reality and virtual reality (AR/VR), allowing for self-assist, work-assist, and remote-assist
Private 5G technology provides several benefits that make it well-suited for supporting augmented reality and virtual reality (AR/VR) applications. Private 5G networks offer high bandwidth and low latency, which are essential for enabling AR/VR experiences that require real-time interaction and response.
With the high-speed and low-latency connectivity provided by private 5G networks, AR/VR applications can offer self-assist, work-assist, and remote-assist capabilities. For example, workers can use AR/VR headsets to receive real-time guidance and assistance while performing complex tasks. This can enhance productivity and accuracy, while also reducing the need for specialized training.
In a manufacturing setting, private 5G networks can support AR/VR applications for remote equipment maintenance, troubleshooting, and repair. With AR/VR headsets, technicians can receive real-time visual guidance from experts located elsewhere, without the need for on-site visits. This can save time and reduce costs, while also minimizing downtime.
Self-assist, work-assist, and remote-assist capabilities are all different ways in which augmented reality and virtual reality (AR/VR) technology can enhance productivity and efficiency in various settings.
- Self-assist capabilities refer to the use of AR/VR technology to provide users with real-time guidance and assistance as they perform complex tasks. For example, an industrial worker wearing an AR headset could receive step-by-step instructions and visual cues to help them assemble a complex machine. This can help reduce errors, increase productivity, and reduce the need for specialized training.
- Work-assist capabilities refer to the use of AR/VR technology to provide real-time assistance to workers as they perform their tasks. For example, an AR headset could provide a worker with real-time data and visualizations about the equipment they are operating, such as temperature, pressure, and other performance metrics. This can help workers identify issues and take corrective action more quickly and efficiently.
- Remote-assist capabilities refer to the use of AR/VR technology to provide remote experts with a real-time view of a worker’s environment, allowing them to provide guidance and support from a remote location. For example, a remote expert could use an AR headset to see what a field technician is seeing and provide guidance on how to troubleshoot and resolve an issue. This can help reduce the need for on-site visits and increase the speed and efficiency of problem resolution.
Overall, the high-speed and low-latency connectivity provided by private 5G networks makes them an ideal solution for supporting AR/VR applications that offer self-assist, work-assist, and remote-assist capabilities to enhance productivity, efficiency, and safety in various settings. Private 5G technology plays a key role in enabling these capabilities by providing the high-speed, low-latency connectivity required for real-time interaction and response.
3. Private 5G technology is revolutionizing the way that autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs) operate in large manufacturing environments by enabling real-time connectivity and control.
One of the main advantages of using Private 5G for AGVs is the low latency and high bandwidth it provides, which allows for real-time communication between the AGV and the central control system. This real-time communication is critical for ensuring that the AGV can respond quickly and accurately to changes in the environment, such as changes in the location of obstacles or changes in the production line.
For example, in a large manufacturing plant, AGVs can be used to transport raw materials or finished products between different areas of the plant. With Private 5G, the AGVs can communicate with the central control system in real-time, allowing for dynamic route planning and adjustments. This can help optimize the flow of materials and reduce the risk of collisions or delays.
Another use case for Private 5G and AGVs is inventory management. By using Private 5G to connect the AGVs to the plant’s inventory management system, the AGVs can be automatically directed to the correct location to pick up or drop off materials. This can help reduce the risk of errors and improve the efficiency of inventory management processes.
Private 5G can also enable new capabilities for AGVs, such as real-time tracking and monitoring. For example, sensors on the AGV can provide real-time data on the vehicle’s location, speed, and orientation, which can be used to optimize the vehicle’s performance and improve safety.
Overall, Private 5G is making real-time connectivity and control possible for AGVs in large manufacturing environments, enabling new levels of efficiency, productivity, and safety. By leveraging the low latency and high bandwidth of Private 5G, manufacturers can optimize their operations and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
4. Computer vision for automatic video surveillance, inspection, and guidance is faster and more efficient on a private 5G network.
Computer vision is a key technology that is being increasingly used in manufacturing environments for tasks such as automatic video surveillance, inspection, and guidance. Private 5G networks can significantly improve the speed and efficiency of computer vision applications by providing high bandwidth and low latency connectivity.
In a manufacturing environment, computer vision can be used for a wide range of applications such as quality control, defect detection, and process monitoring. By using cameras and sensors to capture real-time data, computer vision algorithms can analyze the data to detect defects or anomalies and make decisions about whether to stop the production line or take other actions.
Private 5G networks can greatly enhance the performance of computer vision applications in manufacturing environments. For example, with Private 5G, cameras and sensors can send real-time data to the central processing unit, where computer vision algorithms can analyze the data and make decisions in real time. The low latency of Private 5G ensures that the data is processed quickly, enabling faster detection and response times.
Another advantage of Private 5G for computer vision applications is the high bandwidth it provides. This enables the use of high-resolution cameras and sensors, which can capture more detailed and accurate data. In addition, the high bandwidth of Private 5G can support the use of multiple cameras and sensors simultaneously, allowing for a more comprehensive view of the manufacturing process.
One specific use case for Private 5G and computer vision in manufacturing is quality control. By using cameras and sensors to capture real-time data on production lines, computer vision algorithms can quickly detect defects and anomalies in the products being produced. With Private 5G, this data can be transmitted to the central processing unit in real-time, allowing for immediate corrective action to be taken to prevent defective products from being produced.
Overall, Private 5G networks can greatly improve the speed and efficiency of computer vision applications in manufacturing environments. By providing high bandwidth and low latency connectivity, Private 5G enables faster detection and response times and supports the use of high-resolution cameras and sensors for more accurate data capture.
5. Private 5G Connectivity for Robotics
Robotics systems require fast and reliable connectivity, low latency, and secure communication to operate effectively in industrial settings. While traditional Wi-Fi solutions offer some level of connectivity, Private 5G connectivity offers several advantages that make it a better option for robotics applications. Private 5G networks have higher capacity, which enables them to support a large number of devices and sensors without compromising performance. Additionally, Private 5G networks offer lower latency and faster connectivity compared to Wi-Fi, enabling real-time communication and control for robotics systems. Moreover, Private 5G networks provide a secure and private communication channel that protects against data breaches and cyber attacks, ensuring the safety and integrity of the data being transmitted. Overall, the advanced capabilities of Private 5G connectivity make it the ideal choice for robotics systems in manufacturing industries where speed, reliability, and security are critical factors.
At what Cost
The cost of rolling out a Private 5G network and transitioning into smart manufacturing as per Industry 4.0 standards can vary greatly depending on the specific needs and requirements of each organization. However, it is generally recognized that there will be a significant upfront investment in terms of infrastructure, hardware, software, and personnel.
Some of the main costs associated with rolling out a Private 5G network include the installation of base stations, antennas, and other network equipment, as well as the deployment of edge computing resources to process and analyze data in real-time. In addition, there may be costs associated with the development and integration of custom applications and software, as well as the training of personnel to use and maintain the new technology.
Despite the upfront costs, there are a number of potential benefits to transitioning into smart manufacturing using Private 5G and Industry 4.0 standards. These benefits can include increased efficiency, reduced downtime, improved quality control, and greater flexibility in production processes. By leveraging real-time data analytics and machine learning algorithms, organizations can gain deeper insights into their operations, optimize processes, and make more informed decisions.
Furthermore, as the cost of technology continues to decrease and more organizations adopt smart manufacturing practices, the overall cost of transitioning into Industry 4.0 standards is likely to decrease as well. In addition, there are often government incentives and funding programs available to support the adoption of advanced technologies in manufacturing.
Overall, while the upfront costs of transitioning into smart manufacturing using Private 5G and Industry 4.0 standards can be significant, the potential benefits in terms of efficiency, quality control, and flexibility are significant as well. As technology continues to evolve and costs decrease, the barriers to adoption are likely to become lower, making it more accessible for organizations of all sizes to implement these innovative solutions.